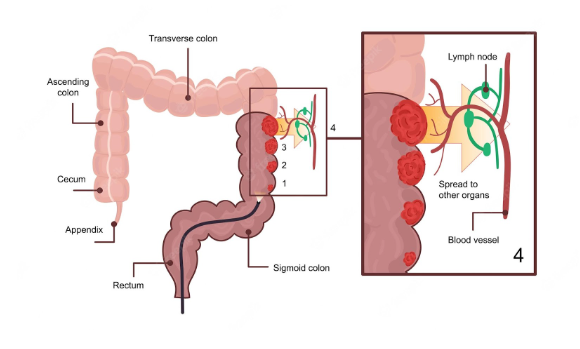
Colorectal cancer (or Colon Cancer) is a type of cancer that affects the colon, which is the final segment of the large intestine. It also affects the rectum, which is the final segment of the small intestine. The disease starts when normal cells in your colon or rectum begin to mutate and grow abnormally. Eventually, these cells can spread to other parts of your body and can become life-threatening if not detected at an early stage and treated promptly. In this article, we will explore more about Colon Cancer — its types, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
In this article Dr. Sandeep Nayak, one of the best surgical oncologist in India will give an insight on colon cancer.
Below we’ll see the definition of a colon cancer,
What is Colon Cancer?
Colon cancer is a disease in which abnormal cells grow in the tissues of the colon. The colon is the last part of the digestive tract and is connected to the anus. If you have colon cancer, you will have abnormal cells growing in the colon. These abnormal cells can grow and spread, if not treated. Colon cancer may be advanced by the time it is diagnosed in many people. It is important to be aware of the early signs and symptoms of colon cancer and to see your doctor if you have any concerns.
Dr. Sandeep Nayak, says, stem cell therapy is an advanced type of treatment that is being used to treat cancer patients as the results are faster and the recovery rate is higher.
Stem cell therapy is the most advanced method of treating cancer as the recovery rate is sooner than the other cancer treatments. Stem cell therapy has been since the 1960, but it was in 2006 that stem cell therapy had a major breakthrough in cancer treatment. Countries like India, Japan and Singapore have some of the advanced stem cell therapy treatments.
Types of Colon Cancer
There are several types of colon cancers, which grow in different ways and respond to different treatment options.
According to Dr sandeep Nayak, one of the best surgical oncologist in India, the main types of colon cancers are:
- Adenocarcinoma: The most common type of colon cancer. More than 95% of all colon cancers are adenocarcinomas. Adenocarcinomas often grow in the innermost lining of the colon.
- Squamous carcinoma: A type of cancer that begins in the squamous cells that make up the surface lining of the colon.
- Mucinous carcinoma: A type of adenocarcinoma that develops in the mucinous cells of the colon.
- Signet ring carcinoma: A type of adenocarcinoma that begins in the submucosal tissues of the colon.
- Neuroendocrine carcinoma: A rare subtype of colon cancer that begins in cells that release hormones, including serotonin and endorphin.
- Large intestine carcinoid: A rare type of adenocarcinoma that develops in the colon or rectum.
Risk Factors for Colon Cancer
- Age: Most people who develop colon cancer are over 50 years old.
- Diet: Eating foods that are high in fat and low in fiber can increase your risk of developing colon cancer.
- Family history: If you have a parent, brother, or sister who has had colon cancer, you may be at an increased risk of developing the disease as well. –
- Race: African American and Hispanic people are more likely to get colon cancer than white people.
- Obesity: People who are obese are more likely to develop colon cancer than people who are not obese.
- Physical activity: People who are physically active have a lower risk of colon cancer than people who are inactive.
- Type of job: People who work in jobs that are dirty or dusty have a higher risk of developing colon cancer.
- Gender: Women have a slightly lower risk of getting colon cancer than men do.
Symptoms of Colon Cancer
- Changes in bowel habits – Abnormal changes in bowel movements are a common symptom of colon cancer. People with colon cancer may have more frequent bowel movements or have fewer bowel movements than normal.
- Changes in appetite – Many people with colon cancer have trouble eating and experience a loss of appetite. This may be due to abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting.
- Weight loss – Weight loss may be a symptom of colon cancer.
- Bloody diarrhea – Blood in the stool is often a symptom of colon cancer, but it can also be a symptom of other conditions.
- Abdominal pain – People with colon cancer may experience abdominal pain. This pain can range from mild discomfort to severe and constant pain.
- General discomfort – People with colon cancer may experience general discomfort or a vague feeling of being unwell.
Diagnosis for Colon Cancer
If you experience any of the above symptoms, consult a doctor. He or she may perform a physical exam, take a medical history, and recommend tests such as imaging tests, blood tests, stool tests, or a combination of these.
Imaging tests include a colonoscopy, endoscopy, X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans. Blood tests can be used to look for certain proteins that are released when the cancer spreads to other parts of the body, says . Dr. Sandeep Nayak, one of the best surgical oncologist in India.
Treatment for Colon Cancer
Treatment depends on the type of colon cancer you have and your overall health. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and biological therapy.
- Surgery: Surgery is the main treatment for colon cancer. A surgeon removes the tumor along with a small amount of healthy tissue around it. The surgeon may remove part or all of the colon.
- Stem cell therapy: Stem cell transplants are procedures that restore blood-forming stem cells in people who have had theirs destroyed by the high doses of chemotherapy or radiation therapy that are used to treat certain cancers.
Blood-forming stem cells are important because they grow into different types of blood cells
- Radiation therapy: A doctor uses special machines to send high-energy rays to the tumor site. This may be used before or after surgery.
- Chemotherapy: Doctors use medications to kill cancer cells. These medications are usually injected into a vein or taken by mouth.
- Targeted therapy: Doctors use medications to block certain proteins that help the cancer grow.
- Immunotherapy: Special injections can help boost the immune system and help fight cancer.
- Biological therapy: Specialized drugs, such as monoclonal antibodies and vaccines, can be used to treat colon cancer.
Conclusion
If you have any symptoms or risk factors for colon cancer, make an appointment to see your doctor. While it’s unlikely that you have colon cancer, it’s important to get it checked out. Early diagnosis and treatment is key to survival.